Australian Thermal Imaging : A Deep Dive into Diverse Applications

Australia, a country known for its rich biodiversity, unique landscapes, and a booming economy, has embraced technology with open arms. One such technology that has penetrated different sectors in the country is thermal imaging. Thermal imaging or thermography involves the use of infrared imaging to analyze temperature variations in objects and environments. In this article, we’ll take a comprehensive look at how thermal imaging is being specifically used across various australian sectors including military, industrial, maritime, security, and more.

Military Applications
Case Study: Enhanced Night Vision for Australian Defense Forces
The Australian Defense Force (ADF) has been utilizing thermal imaging technology for enhanced night vision. Night vision devices with thermal imaging capabilities enable soldiers to detect heat signatures, even in complete darkness or obscured conditions such as smoke or fog. For instance, the LAND 125 Phase 3C project provided the ADF with cutting-edge night vision equipment, including thermal imaging scopes, which significantly enhanced their situational awareness and targeting capabilities.
Drone Surveillance and Reconnaissance
Drones equipped with thermal cameras have also been used by the Australian military for surveillance and reconnaissance missions. These drones can effectively detect human activity or vehicles by their heat signatures, making them particularly effective in detecting hidden or camouflaged targets.
Industrial Applications
Case Study: Thermal Imaging for Predictive Maintenance in Mining

Australia is renowned for its mining industry. Thermal imaging cameras are deployed in mining operations for predictive maintenance. One notable example is the implementation of thermal imaging cameras in the Rio Tinto iron ore mining operations in Pilbara, Western Australia. These cameras are used to monitor the condition of machinery, detecting overheating components before they cause equipment failure.
Agricultural Monitoring

Australia’s agricultural sector also benefits from thermal imaging technology. For instance, farmers use drones equipped with thermal cameras to monitor the health of crops and livestock. These cameras can detect areas in a field that are receiving insufficient water or are infected with diseases, based on temperature variations.
Maritime Applications

Case Study: Monitoring Marine Life around the Great Barrier Reef
Australia is home to the Great Barrier Reef, one of the world’s natural wonders. To protect this precious ecosystem, scientists use thermal imaging cameras mounted on drones and boats. This technology has enabled the identification and monitoring of marine life, including detecting temperature changes in the water that could signify coral bleaching.
Security Sector
Case Study: Australian Airports and Thermal Imaging during COVID-19
During the COVID-19 pandemic, Australian airports employed thermal imaging cameras to screen passengers for elevated body temperatures, which could indicate a fever, one of the symptoms of COVID-19. This was an essential step in early detection and containment of the virus.
Wildlife Conservation

Case Study: Saving the Koalas
Australia’s iconic koalas have been under threat due to habitat loss and bushfires. Conservationists are using drones with thermal imaging cameras to locate and monitor koala populations. These cameras can detect the heat signatures of koalas in the treetops, even at night. This information is critical for formulating conservation strategies.
Emergency Services
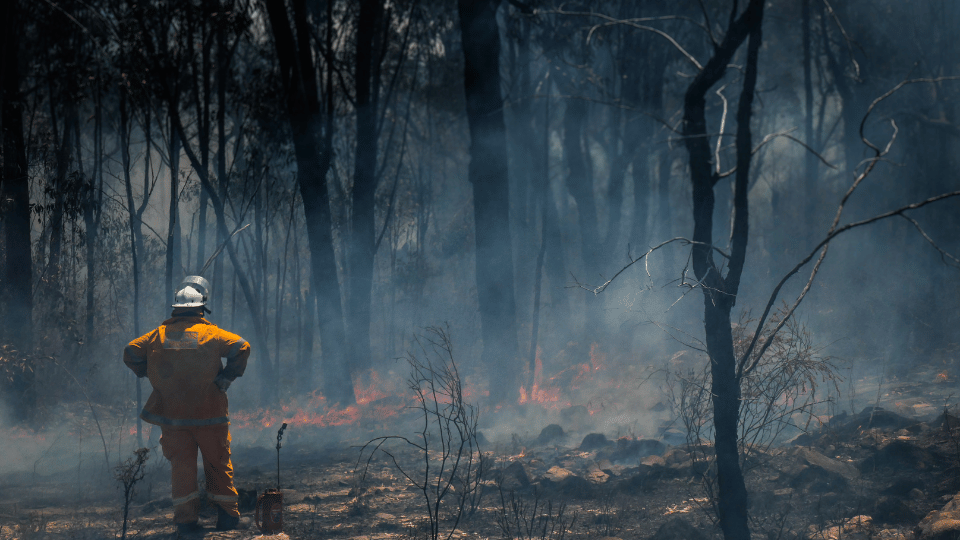

Case Study: Bushfire Management
Australia has historically faced devastating bushfires. Thermal imaging is invaluable for emergency services in detecting and managing these fires. Cameras mounted on helicopters and drones provide real-time information on the spread of fires, enabling better resource allocation and potentially saving lives.
Advancements in Thermal Imaging Technology:
Thermal imaging technology has undergone rapid advancements in recent years. High-resolution sensors have improved the quality of images, while sophisticated image processing algorithms have enabled more accurate temperature readings and analyses. Artificial intelligence (AI) integration has also facilitated the automation of image analysis and decision-making.
Environmental Monitoring and Conservation:
In Australia, thermal imaging is employed for environmental monitoring and conservation. For instance, thermal cameras attached to drones have been used to detect and monitor koala populations, which are particularly vulnerable to climate change and habitat destruction. Moreover, thermal imaging is critical in tracking invasive species, understanding the impact of climate change on ecosystems, and pinpointing sources of pollution.
Energy Efficiency and Building Inspections:
In Australia’s construction sector, thermal imaging plays a vital role in enhancing energy efficiency. By identifying heat leaks and insulation deficiencies, it allows for more targeted improvements in both residential and commercial buildings. This not only reduces energy consumption but also contributes to a more sustainable environment.
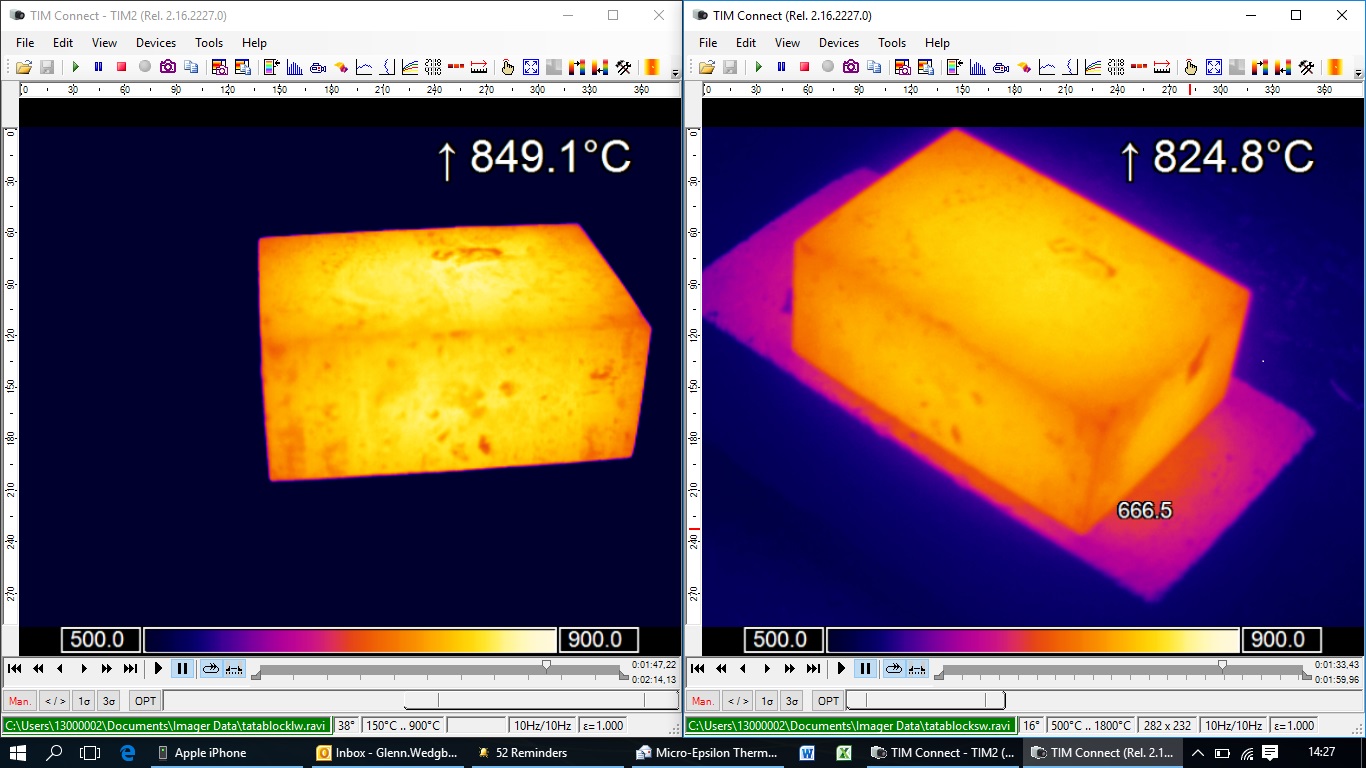
Industrial Applications:
One of the specific case studies in the industrial sector is Tata Steel’s use of Micro-Epsilon thermal imaging cameras in their High Pressure Water Descaling pilot facility. These cameras are used to measure the surface temperature of steel before and after the descaling process to assess descalability and heat loss. Descaling is a process where oxide scale is removed from the hot steel surface through high-pressure water spraying, which is essential for improving the surface quality of rolled products. The thermal imaging cameras have proven to be reliable and easy to use, and are also used in other specific parts of the steel manufacturing process.
Medical and Veterinary Applications:
Australian thermal imaging is increasingly used in the medical field for early detection of diseases and monitoring of patient recovery. For example, a 32-year-old housewife and mother presented with acute back pain with sensory and motor nerve root involvement. Thermography confirmed root irritation, and subsequent scans showed a prolapsed disc. Thermography in this case showed excellent correlation with CT, MRI, and Myelography in radiculopathy. Another example is the use of thermography in detecting post-operative inflammation in a patient who underwent knee surgery. Moreover, thermography has proven useful in detecting and monitoring complex regional pain syndromes and early carpal tunnel syndrome.
Research and Development:
Australia boasts a strong research and development community focusing on thermal imaging. Universities, industries, and government bodies collaborate to further advance thermal imaging technology and explore new applications.
Regulatory Framework and Safety Standards:
In Australia, the use of thermal imaging technology is governed by a regulatory framework that takes into account privacy considerations, data protection, and adherence to safety standards. There are also discussions on the ethical and responsible use of thermal imaging.
Resources
- Thermal imaging cameras case study” from Engineer Live, which provides information on how Tata Steel uses thermal imaging cameras for High Pressure Water Descaling in steel manufacturing1.
- “Case Studies – Be Well Digital Infrared Thermal Imaging” from naplesthermography.com, which offers several case studies on the use of thermal imaging in medical applications, including the detection of radiculopathy, post-operative inflammation, complex regional pain syndromes, and early carpal tunnel syndrome2.