What is MWIR?

Glossary Definition
MWIR, which stands for Mid-Wave Infrared, is a critical region within the infrared spectrum that holds immense significance in various applications, including thermal imaging, remote sensing, and defense technologies. With its unique thermal emission and absorption characteristics, MWIR plays a vital role in detecting and identifying objects based on their temperature differences. In this exploration, we will delve into the significance, working principles, and applications of MWIR technology, shedding light on its diverse uses and contributions across different industries.
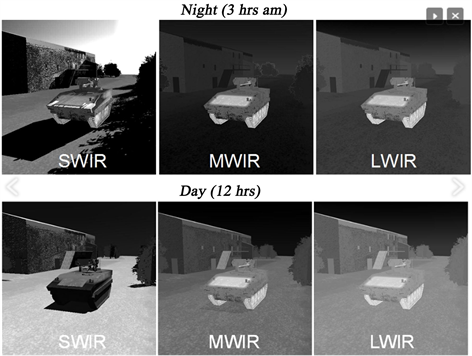
Understanding MWIR
MWIR covers a wavelength range typically between approximately 3 to 5 micrometers (μm) or 3,000 to 5,000 nanometers (nm) within the infrared spectrum. It lies between the short-wave infrared (SWIR) and long-wave infrared (LWIR) regions. MWIR radiation is emitted by objects with temperatures ranging from a few hundred degrees Celsius to several thousand degrees Celsius, making it suitable for various thermal imaging applications.
Working Principles of MWIR Technology
- Thermal Emission: Objects at temperatures above absolute zero emit infrared radiation. MWIR sensors can detect this emitted radiation, allowing them to create images based on the temperature variations of objects.
- Atmospheric Transmission: The MWIR region experiences relatively low absorption by the Earth’s atmosphere, enabling MWIR sensors to operate effectively in various environmental conditions, including through fog, haze, or smoke.
Applications of MWIR Technology
- Thermal Imaging: MWIR finds extensive use in thermal imaging cameras for various applications, including surveillance, security, firefighting, and industrial inspections. Its ability to detect temperature differences makes MWIR valuable in identifying concealed targets and spotting anomalies in machinery or equipment.
- Target Acquisition: In defense and military applications, MWIR sensors are employed for target acquisition and identification. The capability to detect the thermal signatures of vehicles, equipment, or personnel provides an advantage in situational awareness and threat assessment.
- Remote Sensing: MWIR sensors are used in remote sensing applications, such as environmental monitoring, agriculture, and geological surveys. They aid in detecting changes in land and water temperature, identifying vegetation health, and assessing geological features.
- Gas Detection: MWIR technology is utilized in gas detection systems to identify and measure the concentration of specific gases based on their characteristic absorption spectra within the MWIR region.
FAQs:
Q1: How does MWIR differ from other infrared regions? A: MWIR lies between the SWIR and LWIR regions in the infrared spectrum, with specific advantages in terms of atmospheric transmission and thermal detection capabilities.
Q2: What makes MWIR suitable for thermal imaging applications? A: MWIR can detect thermal emissions from objects with temperatures ranging from a few hundred to several thousand degrees Celsius, allowing it to create detailed thermal images.
Q3: Can MWIR sensors operate effectively in challenging environmental conditions? A: Yes, MWIR sensors experience relatively low absorption by the Earth’s atmosphere, enabling them to perform well in adverse conditions like fog, haze, or smoke.
Q4: How is MWIR used in defense and military applications? A: MWIR sensors play a crucial role in target acquisition and identification, enabling military personnel to detect and track objects based on their thermal signatures.
Q5: What are the key advantages of MWIR in remote sensing? A: MWIR aids in monitoring land and water temperature changes, assessing vegetation health, and studying geological features, providing valuable insights for environmental studies.
Q6: Can MWIR sensors detect and measure specific gases? A: Yes, MWIR technology is used in gas detection systems to identify and measure the concentration of gases based on their unique absorption spectra in the MWIR region.
Conclusion
MWIR technology has emerged as a powerful tool with versatile applications in various fields. Its capability to detect thermal emissions and temperature variations provides valuable insights in thermal imaging, remote sensing, gas detection, and defense applications. As advancements in technology continue, MWIR sensors are likely to see further improvements, expanding their potential uses and contributing to a safer, more informed world. The MWIR region within the infrared spectrum remains a crucial area of research and development, driving progress and innovation across multiple disciplines and offering new avenues for exploration and discovery.

